The role of hair extends far beyond function. Hair disorders can significantly impact wellbeing and the quality of life psychologically. In patients undergoing treatment of breast cancer where hair loss is induced by chemotherapy, it has been reported that patients reported the hair loss was mentally more important and difficult than the loss of the breast. In other cases of hair loss, suicide ideation and suicide itself has an increased incidence compared to the general population.
Hair loss is common in the aged population. Androgenetic alopecia is hair loss both in men and women and its prevalence increases with age.
57% of women and 74% of men are affected in the 70-age group.
The human has between 2 and 5 million hair follicles of which 100,000 are on the scalp. No further follicles are generated during the human lifespan. These hair follicles arise from different embryological tissues, the ectoderm, neuroectoderm and mesoderm. Epidermal and mesenchymal cells proliferate and differentiate and cycle through the life cycle of the hair follicle called the anagen, catagen and telogen phases.
Hair Cycles
- Anagen Phase- Hair fiber forms and elongates during this phase
- Catagen Phase- Hair is retained but stops growing
- Telogen Phase- The hair is shed, and the follicle is then empty in a secondary phase called Kenogen
Hair cycling involves these three phases however the upper portion of the hair follicle contains the isthmus and infundibulum which are separated by the sebaceous gland and duct. The hair bulge sits in this area where the erector pili muscle inserts. Overall, this area provides a mechanical barrier to the outside environment and a niche for the stem cells of the hair follicle, keratinocytes, melanocytes and pili myocytes.
These stem cells are activated at the transition from telogen to anagen and promote the regeneration of the bulb.
This activation during this phase ,causes rapid division and gives rise to the outer root sheath, cuticle, cortex and medulla of the new hair shaft. Anagen phase can continue for many years.
Catagen signals a rapid destruction of the entire hair bulb and a complete separation from the dermal papilla within a 2-week period.
During telogen, the bulb and papilla remain connected by a fibrous tract. Cross signaling between the papilla and the bulge in early anagen induces the new bulb to form in the same position as its ancestral bulb.
The dermal papilla also changes during the hair cycle. The dermal sheath which becomes contractile during catagen, pushes the hair follicle and the dermal papilla upwards just below
the bulge. When anagen starts, dermal sheath cells migrate into the dermal papilla and begin the changes in the overall follicle and the cycle begins again.
The development of androgenic alopecia involves the loss of papilla cells into the dermal sheath with each hair cycle leading the miniaturization of the follicle.
Regulation of the Cycle
Regulation of the hair cycle involves multiple autocrine and paracrine pathways in a complex interplay. Anagen to telogen transition is induced by beta catenin signals and is influenced by multiple proteins. These proteins are produced by fibroblasts and adipocytes. The adipocytes precursor cells express platelet derived growth factor which results in hair activation. Other proteins that play a critical part are vascular endothelial growth factor, hepatocyte growth factor and insulin like growth factor. (All contained in PRP).
Through research over the past decade, a new method of cell to cell signaling has been identified by nanosized vesicles called exosomes. These vesicles can transport lipids, metabolites, nucleic acids and proteins. They contain mRNA and have been found to accelerate the onset of anagen and delay catagen.
A recent study identified that human dermal papillae exposed to activated human dermal fibroblasts produce exosomes that resulted in identified enhanced hair follicle growth.
Treatment
The aim of therapeutics is to harness the mechanisms outlined above. This will delay catagen phase, promote and extend the anagen phase and to prevent androgenic alopecia altogether.
Finasteride
Finasteride (Propecia) inhibits the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone. This process is catalyzed by the enzyme 5 alpha reductase. Finasteride is a 5 alpha reductase inhibitor. Side effects of Finasteride limit its use. It is contraindicated in women of childbearing potential since it is teratogenic. Also, it can cause sexual dysfunction in men such as erectile dysfunction, impotence and feminization. The most important side effect is suicidal ideation and suicide. Groups have lobbied the FDA to have it removed from the market altogether, but the FDA only issued a black box warning. Finasteride also must be taken indefinitely. When discontinued, patients reverted to the initial hair loss cycle.
Dutasteride
Dutasteride (Avodart) is a much more potent 5 alpha reductase inhibitor. There are 2 isolated enzymes of the 5 alpha reductase molecules. Avodart is 10 times more potent than finasteride on the first and 100 times more potent on the second. Therefore, the potential for significant increases in the side effect profile are expected. It has not been approved for hair loss by the
FDA. Common side effects include erectile dysfunction, lower sex drive and ejaculation problems.
Minoxidil
Minoxidil was approved initially as an anti-hypertensive drug. Hypertrichosis was identified as an unwanted side effect but prompted the development as a treatment for hair loss. Rogaine was released in the 1980s. Hypotension especially postural hypotension and fluid retention have been the major side effects.
Minoxidil is converted to its active form by sulfotransferase enzymes in the hair follicle. Aspirin, even low dose aspirin, inhibits hair follicle sulfotransferase activity and will impact the response of topical minoxidil application. The efficacy is further limited by poor solubility. Solutions greater than 5% are unstable. Furthermore, crystallization of minoxidil occurs on the scalp when the solvent evaporates. This leaves and unpleasant cosmetic effect on the hair. Finally, minoxidil generally takes 4-6 months to become apparent and continued use is mandatory as discontinued use will revert to initial hair loss. It is not approved for receding hairline.
Red Light Therapy
Low level laser therapy (LLLT) or red-light therapy exerts a bio-stimulation effect on tissue promoting anti-inflammatory effects. This activity improves microcirculation. In studies, LLLT resulted in significant increases in overall hair density.
Another study showed activation of hair follicle stem cell niches, an induction of cell proliferation and an increase in anagen phase duration with LLLT.
Microneedling
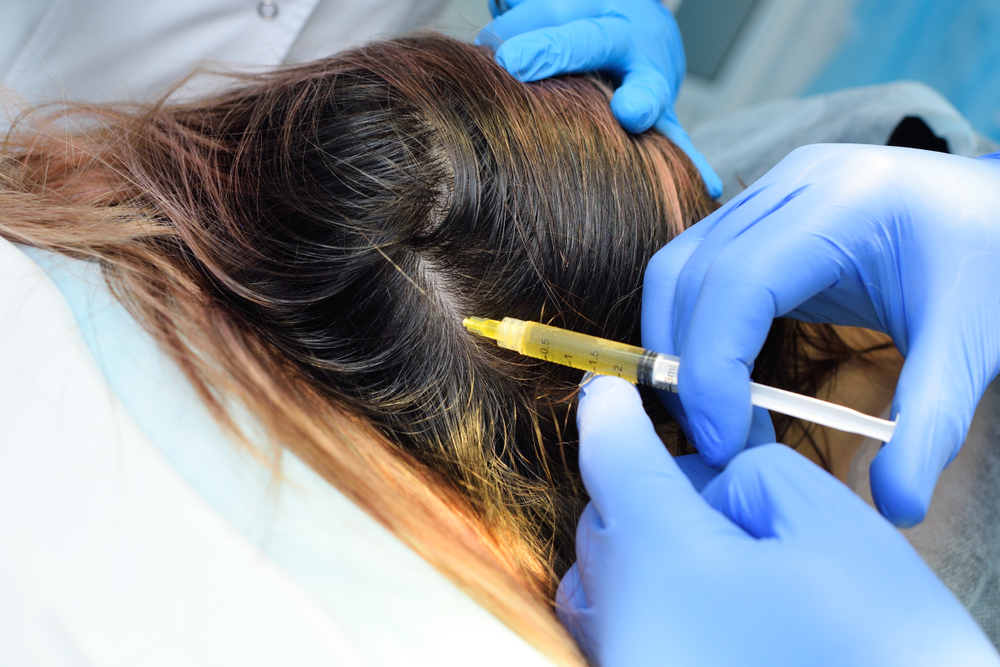
Microneedling is the use of fine needles to micro-puncture the stratum corneum of the epidermis. The procedure alone can stimulate neovascularization, growth factor activity and increased bio-active protein pathways. It is often used with platelet rich plasma or exosomes.
Platelet Rich Plasma
Platelet Rich Plasma is an autologous blood derived concentrate. As such, it is non antigenic and lacks significant side effects. It contains numerous growth factors including platelet derived growth factor, transforming growth factor, vascular endothelial growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, endothelial growth factor, hepatocyte growth factor and insulin like growth factors. Many interleukins and other bio-active proteins are contained in PRP. It has been shown that PRP prolongs anagen, prevents catagen and shortens the period from telogen to anagen through these growth factors and can stimulate cell survival, proliferation and differentiation. Studies highlight evidence of increased hair numbers and thickness in PRP treated groups of patients.
Exosomes
Exosomes are a cell free secretome containing bio-active materials such as growth factors, cytokines, nucleic acids and other factors that play an important role in the hair follicle cycle and regeneration. It has been shown that 80% or more of the transplanted mesenchymal stem cell activity are based on paracrine signaling from exosomes. The exosomes are mediators of tissue repair and regeneration due to activation of signaling pathways and have been proven to be regulators of cell proliferation and apoptosis during tissue regeneration. Exosomes are critical in hair follicle regeneration.
Tissue regeneration has been proven to promote hair growth. Topical treatments have many side effects and must be used continuously for the effect to remain in place. Regenerative treatment protocols have fewer side effects and do not need continuous use for a sustained result. Combination therapies are more beneficial than one treatment alone.
Juventix Regenerative Medical is an industry leader in the regenerative medical field. Our product line includes platelet rich plasma kits, microneedling devices, low level laser therapy, and through our collaborator, Evolutionary Biologics, exosomes. These multiple treatments and devices incorporate all the potential resources needed for the medical professional caring for hair loss clients and exclude the use of topical medications with their significant side effects.
Studies
Regen Ther 2022 Dec;21 527-539 PMID 36382136
Methods Mol Bio 2021;2202:51-61 doi:10.1007/978-1-0716. PMID 32857345
Aesthet Surg J 2018 Jul 13;38(8):811-822 PMID 29554209
J Cosmet Dermatol 2020 May;19(5):1078-1085 PMID 31541565
Fac Rev 2022 Jan 12 doi:10.12703/r/11-1 PMID 35156098