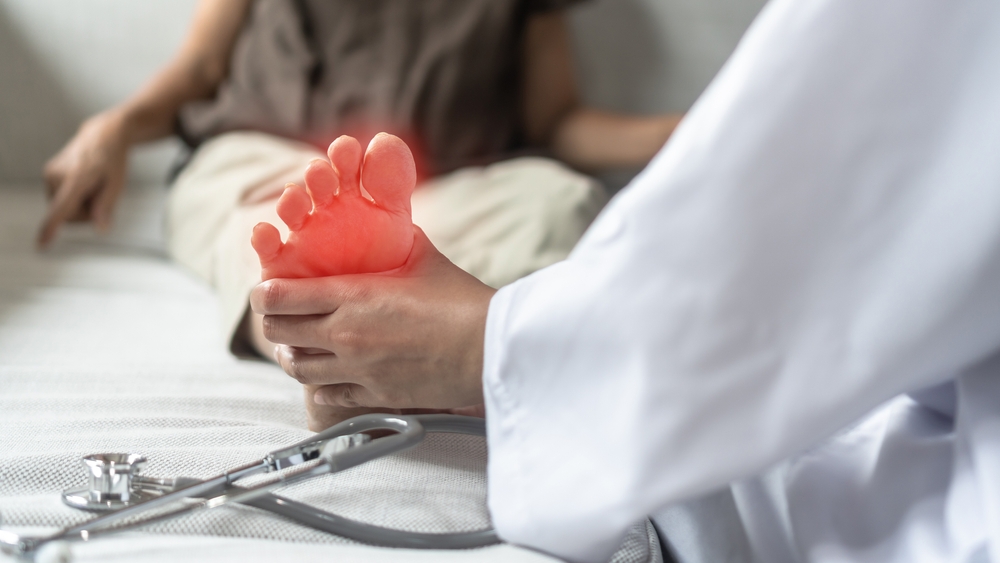
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is a clinical syndrome resulting from damage to the peripheral nervous system. Common symptoms are pain, numbness, tingling and motor dysfunction.
Current standard treatments are aimed at symptom control only. Orthobiologic treatments are currently being used due to their regenerative and healing capabilities.
Causes Of Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy has diverse etiologies:
Metabolic and endocrine disorders with diabetes being the most common.
Genetic disorders such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (a hereditary disease that damages nerves in the legs and arms).
Toxic exposures especially to chemotherapy agents such as vincristine.
Infections such as HIV and leprosy.
Inflammatory/immunologic conditions such as Guillain Barre syndrome.
Nutritional deficiencies like B12 deficiency.
Physical trauma or compression of the nerves such as carpal tunnel syndrome.
Symptoms
Sensory: pain, burning, tingling, numbness, hypersensitivity.
Motor: muscle weakness, unstable gait.
Autonomic: blood pressure fluctuations, bowel and bladder dysfunction.
Orthobiologic Treatments Of Peripheral Neuropathy
Platelet Rich Plasma
Mechanism
Platelet Rich Plasma is an autologous concentrate, rich in growth factors, cytokines and bioactive proteins. These molecules modulate inflammation and support tissue regeneration.
A few of these growth factors include: EGF, VEGF, IGF-1 and TGF-beta.
Epidermal Growth Factor – is a small protein that acts as a signaling molecule telling cells to grow, divide and differentiate and triggers repair and cell survival.
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor – this protein stimulates the growth of new blood vessels and lymphatic vessels.
Insulin Growth Factor-1 – in nerve tissue IGF-1 promotes cell growth and protects from breakdown.
Transforming Growth Factor Beta – is a multifunctional cytokine that regulates a wide range of cellular processes including cell growth and differentiation.
Clinical evidence
Animal studies demonstrate that PRP enhances Schwann cell support, remyelination and nerve regeneration in models of nerve damage.
A systematic review concluded PRP is more effective than conservative treatments for carpal tunnel syndrome in short and mid-term outcomes.
In diabetic peripheral neuropathy, PRP is more effective in improving pain, sleep quality and overall function when compared to pregabalin (Lyrica) or gabapentin (Neurontin).
In severe peripheral neuropathic cases (e.g., leprosy patients) about 39 out of 45 (87%) experienced 70% pain reduction greater than 3 months with PRP therapy.
In most studies, meaningful symptom relief and function improvements were noted with PRP over other treatments.
Stem Cells
Mechanism
Mesenchymal stem cells exert therapeutic effects via:
Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory cytokine release such as Interleukin-10 and TGF-beta and reducing proinflammatory mediators such as IL-1, IL-6 and TGF-alpha.
Migration to injury sites, trophic support and differentiation into neural or support cells.
Paracrine effects, including extracellular vesicles/exosomes carrying proteins, mRNA that promote neuronal regeneration.
In animal models with nerve injury mimicking diabetic neuropathy, MSC reduced hyperalgesia/allodynia and improved nerve function and conduction metrics.
Muse cells – a subpopulation of stem cells administered intrathecally achieved superior analgesic impact in animal studies.
One estimate in a non-peer-reviewed study suggested improvement in up to 80% of treated patients.
Exosomes (Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells)
Mechanism
Exosome therapy delivers regenerative signals by growth factors, cytokines and mRNA contained on them and this supports neuronal survival, reducing inflammation and enhancing neural regeneration.
These are derived from mesenchymal stem cells, so the effect is similar.
Exosomes are anti-inflammatory, support cell regeneration and differentiation into new tissue.
Exert Therapeutic Effects
Anti-inflammatory.
Bactericidal.
Promote angiogenesis.
Optimize collagen alignment.
Facilitate regeneration of neuronal tissue.
Exosome utility is strongly supported by clinical studies. Extracellular vesicles not only possess regenerative properties but serve as effective carriers for bioactive peptides and proteins.
Peptides
Peptides are short chains of two or more amino acids that are linked by peptide bonds. More than 7000 naturally occurring peptides that have critical roles in human physiology and performance have been identified. They work as hormones, neurotransmitters, growth factors, ion channel ligands or anti-infectives in the body. Peptides cause a cell signaling response that can have regulatory and rejuvenation actions on neuroendocrine immune function. Peptides can help the body recover from an injury or illness faster, lose weight more effectively, decrease inflammation and pain.
Peptides influence nerve health through several mechanisms beneficial in managing neuropathy. Some peptides promote the regrowth and repair of damaged nerve fibers – a process known as nerve regeneration. This regeneration capacity is an important area of current research for restoring nerve function. Many peptides also exhibit anti-inflammatory properties as inflammation contributes to nerve damage and neuropathic pain. By reducing inflammatory responses, peptides help protect existing nerve cells from further degeneration. This neuroprotective effect preserves nerve integrity. Peptides can also modulate pain signals offering relief from neuropathic pain. They interact with pain receptors or signaling pathways altering how pain is perceived. This multifaceted influence on nerve health – encompassing regeneration, anti-inflammatory actions, neuroprotection, and nerve and pain modulation – makes peptides a valuable area of study for neuropathic treatments.
Key Peptides In Neuropathy
ARA290
ARA290 is an eleven amino acid peptide derived from erythropoietin. Designed to avoid erythropoietin’s effects like increased red blood cell production, it selectively activates the innate repair receptor complex formed by the beta common receptor and the EPO receptor. This activation triggers anti-inflammatory pathways and promotes tissue repair, leading to a reduction in neuropathic pain symptoms and an increase in small nerve fiber density.
Nerve Growth Factor (NGF)
Nerve growth factor is a neurotrophin that supports the survival, growth and differentiation of neurons. NGF plays a role in the development and maintenance of the nervous system and is involved in the sensitization of pain pathways in neuropathic pain syndromes such as peripheral neuropathy.
BPC 157
BPC157 is a pentadecapeptide that originates from gastric juice. It is known for its regenerative and anti-inflammatory properties and has been studied for tissue repair. BPC157 promotes nerve regeneration, as shown in studies after peripheral nerve transection, and has neuroprotective effects influencing growth factors and promoting collagen formation.
TB-500
TB-500, also known as Thymosin Beta-4, is a synthetic 43 amino acid peptide. It promotes cell migration, blood vessel formation and tissue repair in nerve health. TB-500 enhances the repair of oligodendrocytes and astrocytes which support neurons and reduces glial scarring, a barrier to nerve regeneration. It also possesses anti-inflammatory effects that contribute to neurological recovery.
Cerebrolysin
Cerebrolysin is a mixture of enzymatically treated peptides and amino acids derived from pig brain. It is used clinically in some countries for neurodegenerative conditions due to its neurotrophic and neuroprotective effects. Cerebrolysin acts similarly to endogenous neurotropic factors, supporting neural networks and promoting nerve regeneration by stimulating pathways involved in brain plasticity and axon growth. It also protects the vascular system and reduces neuroinflammation.
Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment
PRP Therapy For Nerve Regeneration
Platelet Rich Plasma is an autologous blood-derived concentrate, rich in cytokines, growth factors and bioactive proteins. Platelet Rich Plasma is well known and studied for its regenerative potential. In peripheral neuropathy, PRP demonstrated positive effects on healing of nerve function as well as histological improvements on cut peripheral nerve injury models.
J Craniofac Surg 2017 Jan;28(1):e49-57 PMID 27893553
Stem Cell And Exosome Research
Stem cell-derived exosomes and mesenchymal stem cells have been studied in treating autoimmune and neurodegenerative diseases. Studies have shown mixed results. It was felt due to the size of stem cells, exosomes derived from stem cells would be a better smaller option. The exosomes were then tested and found to be efficacious. The testing found that stem cell-derived exosomes served as cell-free therapies for autoimmune and nervous system disorders.
ACS Nano 2019 Jun 25;13(6):6670-6688 PMID 31117376
Peptide Therapy And GLP-1 Benefits
Peptide therapy is currently under investigation in many research facilities. The results are very promising. GLP-1, which are currently being used for diabetes and weight reduction, have shown to have many other advantages. These agents have shown reversal of nephropathy, retinopathy and neuropathy. Well-designed studies are clarifying the benefit of these and other peptide compounds.
Diabetologia 2023 Oct;66(10):1832-1845 PMID 37597048
Juventix Regenerative Medical Solutions
PRP Kits And Devices For Neuropathy
Juventix Regenerative Medical provides high quality platelet rich plasma kits and devices for treatment of peripheral neuropathy. Our PRP kits are FDA cleared and designed for safety, sterility and effectiveness.
LED Activator For Enhanced Cytokine Release
Juventix Regenerative Medical provides a LED Activator, which utilizes polychromatic light to enhance the release of cytokines and growth factors from the alpha granules on the platelets. This method is especially important in treating diseases such as diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
Apollo Duet For Non-Invasive Delivery
Juventix Regenerative Medical offers the Apollo Duet. This innovative device employs the combination of electroporation and ionophoresis to drive molecules into the deeper aspects of the skin without the utilization of a needle. This technology would be extremely efficacious in those who have needle phobia or patients with peripheral vascular disease and subject to infections in the distal areas of the limbs.
Peptides For Research And Regenerative Innovation
Juventix Regenerative Medical is proud to offer peptides for research purposes. PubMed currently is listing 12,465 studies and articles concerning the use of peptides. Peptides are the wave of the future in medicine and regeneration. Along with exosomes, platelet rich plasma kits and devices and now peptides, Juventix is poised to assist the regenerative professional to achieve greater outcomes for their patients, especially those with neuropathy.
Restore, Revive, Regenerate – Juventix Regenerative Medical
Regenerative regards,
Dr. Robert McGrath